33 二叉树的中序遍历
中序遍历是先左子树,再根节点,最后是右节点的顺序。递归的写法比较直观:
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode root){
if (root == null){
return;
}
dfs(root.left); // 先遍历左子树
ans.add(root.val); // 保存根节点的值
dfs(root.right); // 再遍历右子树
}迭代的版本就是使用一个栈,模拟递归的过程:
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
Deque<TreeNode> st = new ArrayDeque<>();
while (root != null || !st.isEmpty()){
// 先一直遍历左子树
while (root != null){
st.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
// 左子树遍历结束,保存根节点的值
root = st.pop();
ans.add(root.val);
// 切换到右子树继续遍历
root = root.right;
}
return ans;
}34 二叉树的最大深度
根节点的深度为 0,其他节点的深度是左右子树的最大深度 + 1。
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null){
return 0;
}
int l = maxDepth(root.left);
int r = maxDepth(root.right);
return Math.max(l, r) + 1;
}35 翻转二叉树
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
// 空节点不用翻转
if (root == null){
return root;
}
// 翻转左子树
TreeNode left = invertTree(root.left);
// 翻转右子树
TreeNode right = invertTree(root.right);
// 翻转当前节点
root.left = right;
root.right = left;
return root;
}36 对称二叉树
除去根节点的两颗左右子树是对称二叉树的关键信息在于:
两颗子树的根节点相同;
一棵树的左子树和另一颗数树右子树相同;
一棵树的右子树和另一颗数树左子树相同。
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (p == null || q == null){
return p == q;
}
return p.val == q.val && isSameTree(p.left, q.left) && isSameTree(p.right, q.right);
}37 二叉树的直径
int ans = 0;
public int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
public int dfs(TreeNode root){
// 叶子节点链长为 0,空节点链长为 -1
if (root == null){
return -1;
}
int l = dfs(root.left) + 1; // 左子树最大链长
int r = dfs(root.right) + 1; // 右子树最大链长
ans = Math.max(ans, l + r); // 两链拼成路径
return Math.max(l, r); // 当前子树最大链长
}38 二叉树的层序遍历
使用队列(Queue)按层遍历二叉树。
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null){
return ans;
}
// 创建队列,插入根节点
Deque<TreeNode> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
q.offer(root);
while(!q.isEmpty()){
// 按层遍历
int n = q.size();
List<Integer> layer = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
TreeNode node = q.poll();
layer.add(node.val);
if (node.left != null) q.offer(node.left);
if (node.right != null) q.offer(node.right);
}
ans.add(layer);
}
return ans;
}39 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
return dfs(nums, 0, nums.length);
}
// 把 [left, right - 1] 转换成二叉搜索树
private TreeNode dfs(int[] nums, int left, int right){
if (left == right){
return null;
}
int m = left + (right - left) / 2;
return new TreeNode(nums[m], dfs(nums, left, m), dfs(nums, m + 1, right));
}40 验证二叉搜索树 ⭐
通过数值的区间范围来验证二叉搜索树。
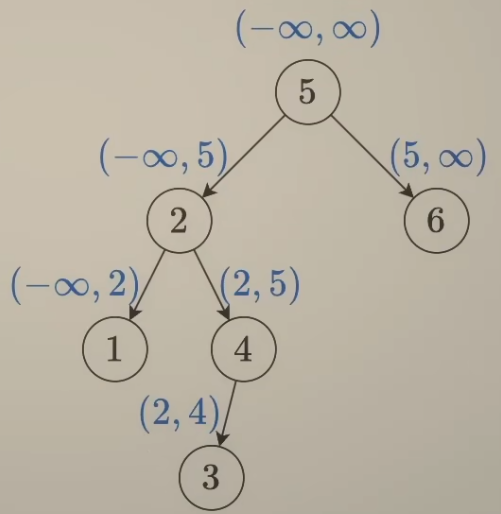
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
return isValidBST(root, Long.MIN_VALUE, Long.MAX_VALUE);
}
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root, long left, long right) {
if (root == null) {
return true;
}
int x = root.val;
return left < x && x < right &&
isValidBST(root.left, left, x) &&
isValidBST(root.right, x, right);
}41 二叉搜索树中第 K 小的元素 ⭐
二叉搜索树的中序遍历就是从小到大遍历的,中序遍历过程中第 k 个出现的元素就是答案。
int k;
int ans;
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
this.k = k;
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode root){
if (root == null || k == 0){
return;
}
dfs(root.left);
if (--k == 0){
ans = root.val;
}
dfs(root.right);
}42 二叉树的右视图
使用层序遍历,将每一层的最后一个元素加入答案即可。
public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null){
return ans;
}
Deque<TreeNode> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
q.offer(root);
while (!q.isEmpty()){
int n = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++){
TreeNode node = q.poll();
// 最右侧元素,加入答案
if (i == n - 1){
ans.add(node.val);
}
if (node.left != null) q.offer(node.left);
if (node.right != null) q.offer(node.right);
}
}
return ans;
}本题也可以使用 DFS 解决,具体思路:先递归右子树,再递归左子树,当某个深度首次到达时,对应的节点就在右视图中。
public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(root, ans, 0);
return ans;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode root, List<Integer> ans, int depth) {
if (root == null){
return;
}
// 首次到达某个深度
if (ans.size() == depth){
ans.add(root.val);
}
dfs(root.right, ans, depth + 1);
dfs(root.left, ans, depth + 1);
}43 二叉树展开为链表
头插法,从最后一个节点开始,依次向前插入节点。因此需要「右子树-左子树-根节点」的顺序 DFS 遍历树。
TreeNode head;
public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null){
return;
}
flatten(root.right);
flatten(root.left);
root.left = null;
root.right = head;
head = root;
}44 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树 ⭐
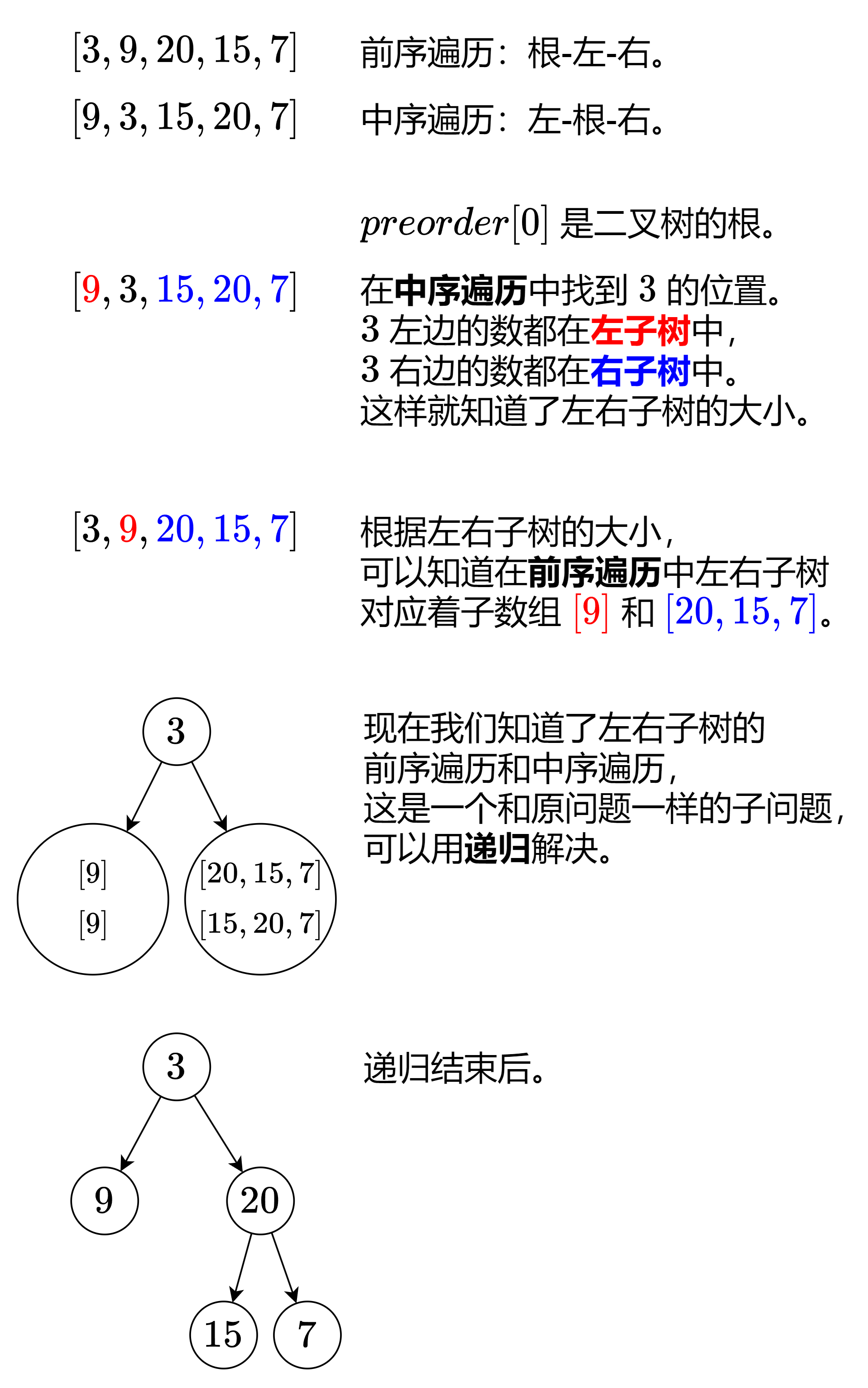
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
// 中,左,右
// 左,中,右
int n = preorder.length;
if (n == 0){
return null;
}
// 左子树的大小
int leftSize = indexOf(inorder, preorder[0]);
int[] preL = Arrays.copyOfRange(preorder, 1, 1 + leftSize);
int[] preR = Arrays.copyOfRange(preorder, 1 + leftSize, n);
int[] inL = Arrays.copyOfRange(inorder, 0, leftSize);
int[] inR = Arrays.copyOfRange(inorder, leftSize + 1, n);
TreeNode left = buildTree(preL, inL);
TreeNode right = buildTree(preR, inR);
return new TreeNode(preorder[0], left, right);
}
public int indexOf(int[] a, int x){
for (int i = 0; ; i++){
if (a[i] == x){
return i;
}
}
}45 路径总和 III
int ans;
int targetSum;
Map<Long, Integer> cnt = new HashMap<>();
public int pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
cnt.put(0L, 1);
this.targetSum = targetSum;
return dfs(root, 0);
}
public int dfs(TreeNode root, long sum) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
sum += root.val;
int res = cnt.getOrDefault(sum - targetSum, 0);
cnt.merge(sum, 1, Integer::sum);
res += dfs(root.left, sum);
res += dfs(root.right, sum);
cnt.merge(sum, -1, Integer::sum); // 恢复现场
return res;
}46 二叉树的最近公共祖先
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (root == null || root == p || root == q){
return root;
}
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
if (left != null && right != null){
return root;
}
return left != null ? left : right;
}47 二叉树中的最大路径和
int ans = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
public int maxPathSum(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
public int dfs(TreeNode root){
if (root == null){
return 0;
}
int leftVal = dfs(root.left);
int rightVal = dfs(root.right);
ans = Math.max(ans, leftVal + rightVal + root.val);
return Math.max(Math.max(leftVal, rightVal) + root.val, 0);
}参考
部分思路参考了力扣官方题解和灵茶山艾府题解。


